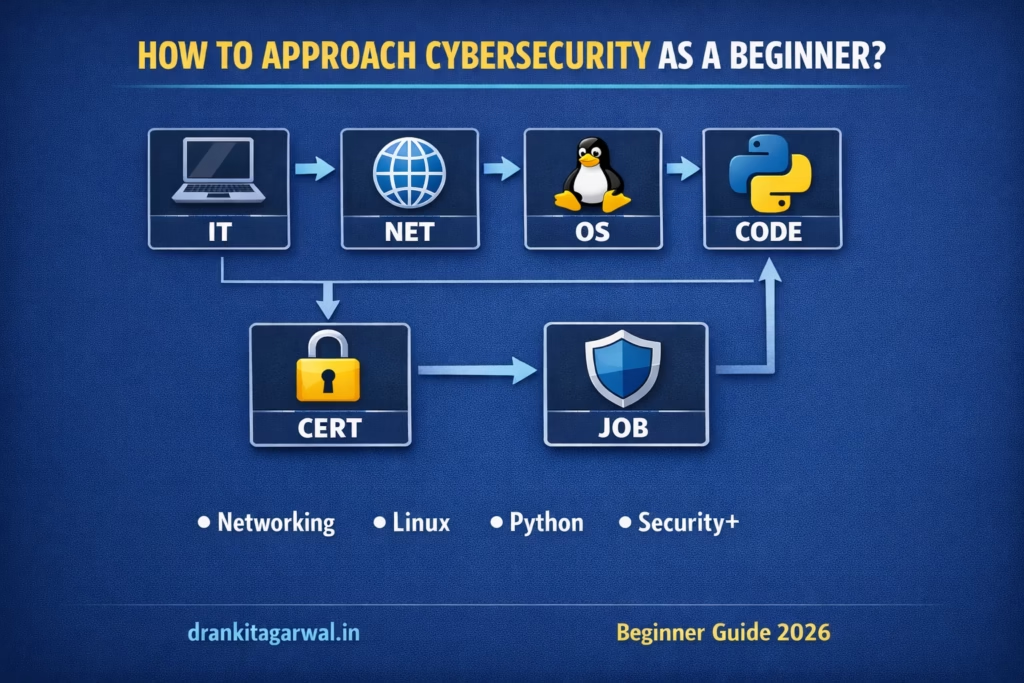
How Should I Approach
Cybersecurity as a Beginner?
A comprehensive, step-by-step roadmap to launch your cybersecurity career from scratch. No prior experience needed — just curiosity and determination.
Table of Contents
- 01 What Is Cybersecurity?
- 02 Why Learn Cybersecurity?
- 03 Build IT Foundations
- 04 Learn Networking
- 05 Master Operating Systems
- 06 Learn Programming
- 07 Core Security Concepts
- 08 Hands-On Practice
- 09 Certifications
- 10 Stay Updated
- 11 Choose Specialization
- 12 Common Mistakes
- 13 6-Month Roadmap
- 14 Free Resources
- 15 FAQs
What Is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting systems, networks, programs, and data from digital attacks, unauthorized access, damage, or theft. It encompasses everything from securing your personal email account to defending critical national infrastructure.
Network Security
Protecting network infrastructure from unauthorized access and threats
Application Security
Securing software applications from vulnerabilities
Cloud Security
Protecting data and systems in cloud environments
Incident Response
Detecting, analyzing, and responding to security incidents
Information Security
Protecting the confidentiality and integrity of data
Identity Management
Managing user access and authentication
Why Should You Learn Cybersecurity?
- High Demand: Over 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity jobs worldwide, making it one of the most in-demand career fields.
- Lucrative Salaries: Average cybersecurity analyst salary in India ranges from ₹5 LPA to ₹25+ LPA depending on experience.
- Work From Anywhere: Many cybersecurity roles are fully remote, offering global opportunities.
- Make a Real Impact: You're literally protecting people, businesses, and governments from harm.
- Continuous Learning: The field is always evolving, so you'll never be bored.
Step 1: Build a Strong Foundation in IT Basics
Before diving into cybersecurity, you need to understand how computers and technology work at a fundamental level. This foundation is crucial for everything that comes after.
📚 What to Learn:
- How computers work — CPU, RAM, storage, BIOS/UEFI
- How the internet works — DNS, HTTP/HTTPS, IP addresses, ISPs
- Basic hardware and software concepts
- File systems and data storage
- Virtualization basics — VMware, VirtualBox
🎓 Recommended Resources:
Pro Tip: Set up a virtual lab on your computer using VirtualBox. Install different operating systems and start experimenting. Hands-on learning beats theory every time!
Step 2: Learn Networking Fundamentals
Networking is the backbone of cybersecurity. Almost every cyberattack involves a network in some way. You cannot secure what you don't understand.
🔑 Key Networking Concepts:
🏗️ Core Models
- OSI Model (7 Layers)
- TCP/IP Model
- IP Addressing & Subnetting
🔧 Protocols & Services
- DNS, DHCP, NAT
- TCP, UDP, HTTP/S, FTP
- SSH, SMTP, SNMP
🛡️ Security Components
- Firewalls & Routers
- VPNs & Proxy Servers
- Packet Analysis (Wireshark)
🎓 Recommended Certifications:
Step 3: Understand Operating Systems
You need to be comfortable with multiple operating systems, especially Linux, which is heavily used in cybersecurity for penetration testing, forensics, and server management.
🐧 Linux (Most Important)
- Command line proficiency
- File permissions & user management
- Process management
- Kali Linux for pentesting
- Ubuntu/Debian for servers
🪟 Windows
- Command Prompt & PowerShell
- Active Directory basics
- Windows Registry
- Event logs & monitoring
- Group Policies
How to Practice: Install Kali Linux and Ubuntu on VirtualBox. Complete the Linux Journey free course and practice on OverTheWire: Bandit wargame.
Step 4: Learn Programming & Scripting
You don't need to be a software developer, but knowing how to code gives you a significant edge in cybersecurity for automation, tool development, and understanding exploits.
💻 Languages to Prioritize:
| Language | Why It Matters | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| Python | Automating tasks, writing security tools, scripting exploits | Must Learn |
| Bash | Linux scripting and automation | Must Learn |
| PowerShell | Windows administration and attack scripting | Important |
| JavaScript | Understanding web vulnerabilities (XSS, etc.) | Important |
| SQL | Understanding SQL injection attacks | Important |
| C/C++ | Understanding buffer overflows and low-level exploits | Good to Know |
Start With Python: It's the #1 recommended language for cybersecurity beginners. Easy to learn, versatile, and widely used for writing security scripts, automating tasks, and building hacking tools.
Step 5: Dive into Core Cybersecurity Concepts
Now that you have the fundamentals, it's time to learn cybersecurity-specific concepts that form the backbone of the entire field.
🔐 Security Fundamentals
- CIA Triad — Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability
- Authentication vs. Authorization
- Encryption — Symmetric vs. Asymmetric
- Hashing — MD5, SHA-256
- Digital Certificates & PKI
- Security Frameworks — NIST, ISO 27001
🦠 Types of Cyber Threats
Malware
Viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, spyware
Phishing
Social engineering & deceptive emails
MITM Attacks
Man-in-the-Middle interception
DoS/DDoS
Denial of Service attacks
SQL Injection
Database manipulation attacks
Zero-Day
Unknown vulnerability exploits
Step 6: Get Hands-On Practice
Cybersecurity is a hands-on field. Reading theory alone won't make you job-ready. You need to practice in safe, legal environments to build real skills.
🎯 Best Platforms for Practice:
| Platform | What It Offers | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| TryHackMe | Beginner-friendly guided rooms & learning paths | Free + Premium |
| Hack The Box | Real-world hacking challenges & machines | Free + Premium |
| OverTheWire | Linux & networking wargames | Free |
| PicoCTF | Capture The Flag for beginners | Free |
| CyberDefenders | Blue team (defense) challenges | Free |
| DVWA | Damn Vulnerable Web Application | Free |
| VulnHub | Downloadable vulnerable VMs | Free |
| OWASP WebGoat | Web security practice application | Free |
Beginner Path: Start with TryHackMe's "Complete Beginner" learning path. It's structured, guided, and perfect for absolute beginners. Then move to Hack The Box when you're more confident.
🏠 Build Your Own Home Lab:
- Use VirtualBox or VMware to create virtual machines
- Set up Kali Linux as your attack machine
- Set up Metasploitable or DVWA as your target
- Practice scanning, enumeration, exploitation, and reporting
Step 7: Pursue Cybersecurity Certifications
Certifications validate your knowledge and are often required by employers. Here's a structured roadmap from beginner to advanced.
🟢 Beginner Certifications:
- CompTIA Security+ — The gold standard entry-level certification
- Google Cybersecurity Certificate — Excellent for absolute beginners (Coursera)
- CompTIA CySA+ — For aspiring Security Analysts
- CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) — Popular but more theoretical
🟡 Intermediate Certifications:
- eJPT — Practical, hands-on Junior Penetration Tester
- CompTIA PenTest+ — Penetration testing focus
- Blue Team Level 1 (BTL1) — Defense-oriented
🔴 Advanced Certifications:
- OSCP — Highly respected, 100% practical exam
- CISSP — For experienced professionals (management-level)
- CISM / CISA — Governance and audit focus
📍 Recommended Certification Path:
Step 8: Stay Updated & Join the Community
Cybersecurity evolves daily. New vulnerabilities, tools, and techniques emerge constantly. Staying updated is not optional — it's essential.
📰 News & Blogs
- Krebs on Security
- The Hacker News
- Dark Reading
- BleepingComputer
- drankitagarwal.in
🎙️ Podcasts
- Darknet Diaries
- Security Now
- CyberWire Daily
📺 YouTube Channels
- NetworkChuck
- John Hammond
- The Cyber Mentor
- David Bombal
- LiveOverflow
👥 Communities to Join:
Step 9: Choose Your Cybersecurity Specialization
Cybersecurity is vast. As you gain experience, you'll want to specialize in an area that excites you. Here are the main career paths:
🔴 Red Team (Offensive)
- Penetration Tester
- Ethical Hacker
- Exploit Developer
- Red Team Operator
- Bug Bounty Hunter
🔵 Blue Team (Defensive)
- SOC Analyst
- Incident Responder
- Threat Hunter
- Digital Forensics Analyst
- Malware Analyst
🟣 Specialized Roles
- Cloud Security Engineer
- App Security Engineer
- GRC Analyst
- Security Architect
- Cryptographer
Don't Know Which to Choose? Start with a SOC Analyst role — it's the most common entry-level position and gives you broad exposure to both offense and defense.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make (Avoid These!)
- Skipping the fundamentals — Jumping straight to hacking without understanding networking or OS basics.
- Certification hoarding — Collecting certifications without actual skills. Focus on learning, not just passing exams.
- Only watching tutorials — Passive learning doesn't work. You must practice actively.
- Trying to learn everything at once — Cybersecurity is massive. Focus on one area at a time.
- Ignoring soft skills — Communication, report writing, and teamwork are critical in cybersecurity roles.
- Not networking — Join communities, attend conferences, and connect with professionals on LinkedIn.
- Illegal hacking — NEVER practice on systems you don't have explicit permission to test. Use legal platforms only.
Important: Unauthorized hacking is a criminal offense. Always practice on platforms designed for learning (TryHackMe, HTB, etc.) or on your own home lab. Never attack real systems without written permission.
Your 6-Month Beginner Roadmap
Here's a condensed, actionable timeline to follow. Consistency is key — dedicate at least 1-2 hours daily.
📅 Month 1-2: Foundations
- Learn IT basics and how computers work
- Study networking (OSI model, TCP/IP, protocols)
- Get comfortable with Linux command line
- Set up VirtualBox with Kali Linux and Ubuntu
📅 Month 3: Programming + Security Basics
- Learn Python basics
- Study CIA Triad, encryption, and common threats
- Start TryHackMe "Complete Beginner" path
📅 Month 4: Hands-On Practice
- Practice on TryHackMe, DVWA, and OverTheWire
- Build and configure your home lab
- Begin CompTIA Security+ preparation
📅 Month 5: Certification Prep
- Intensive Security+ study sessions
- Take practice exams regularly
- Continue hands-on labs alongside study
📅 Month 6: Certification + Job Prep
- Pass CompTIA Security+
- Build portfolio (GitHub, blog, CTF writeups)
- Update LinkedIn and craft your resume
- Start applying for entry-level roles
Free Resources to Get Started Today
Here's a curated list of completely free resources to begin your cybersecurity journey right now:
| Resource | What You'll Learn | Type |
|---|---|---|
| TryHackMe | Beginner cybersecurity fundamentals | Platform |
| Google Cybersecurity Cert | Complete foundations course | Course |
| Professor Messer | CompTIA Security+ prep | Video |
| Cybrary | Various security courses | Platform |
| OWASP Top 10 | Web application security | Guide |
| Cisco Networking Academy | Networking basics | Course |
| Linux Journey | Linux fundamentals | Tutorial |
| OverTheWire: Bandit | Command line practice | Wargame |
| PicoCTF | Beginner CTF challenges | CTF |
| SANS Cyber Aces | Security fundamentals | Course |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Final Thoughts
Breaking into cybersecurity might seem daunting, but remember — every expert was once a beginner. The cybersecurity industry needs passionate, dedicated people like you.
🔑 Key Takeaways
- Start with the fundamentals — Don't rush past networking, OS, and IT basics.
- Be consistent — Dedicate at least 1-2 hours daily to learning.
- Practice, practice, practice — Hands-on experience is everything in this field.
- Stay curious — The best cybersecurity professionals never stop learning.
- Be patient — It's a marathon, not a sprint. Trust the process.
If you follow this roadmap with consistency and determination, you will break into the cybersecurity field. Good luck on your journey! 🚀
Found this guide helpful? Share it with someone who's thinking about starting their cybersecurity journey!